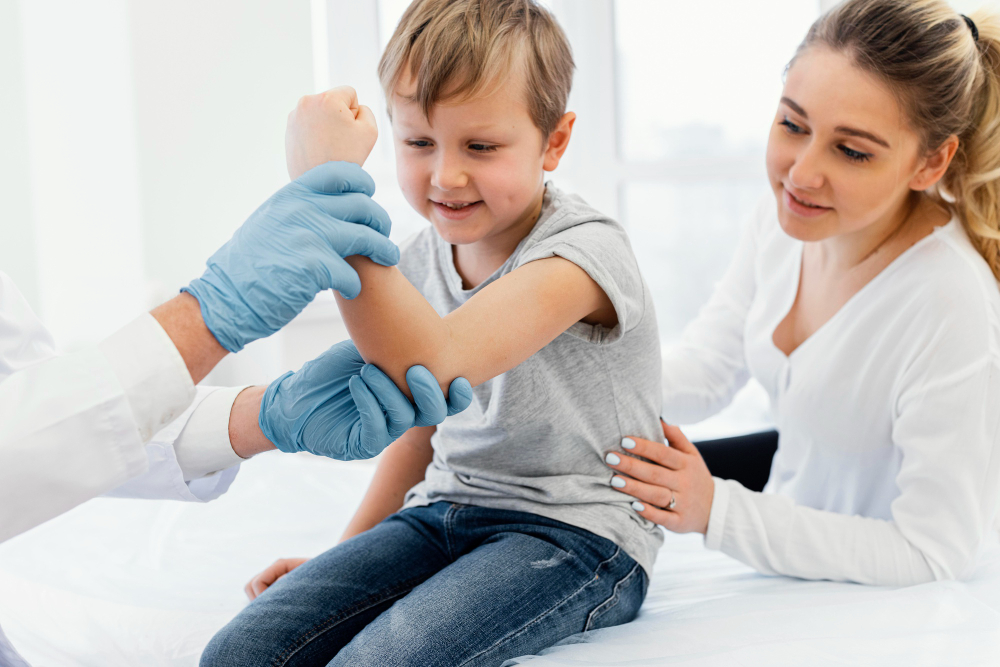
Pediatric fractures are broken bones that happen in children. These injuries are common because kids are active and their bones are still growing. In fact, the World Health Organization notes that falls and accidents are leading causes of pediatric fractures. Early care is important to help bones heal well. In this blog, you will learn about the causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment of pediatric fractures. You will also find tips for prevention and home care. If you are worried about child bone injury, this guide can help you understand what to do next.
Causes of Pediatric Fractures
Children break bones more often than adults. Their bones are softer and more flexible. However, several causes can lead to pediatric fractures. Understanding these causes can help prevent injuries.
Symptoms of Pediatric Fractures
It is important to spot fracture symptoms in kids early. Quick action can help bones heal better. Look for these signs if you think your child has a broken bone:
But not all fractures look obvious. Sometimes, children may only limp or refuse to use the limb. Therefore, always watch for changes in how your child moves or acts.
Diagnosis of Pediatric Fractures
Doctors use several steps to diagnose pediatric fractures. Early diagnosis helps prevent long-term problems. Here is what you can expect during a visit:
With these steps, doctors can find the type and location of the fracture. This helps them choose the best treatment.
Treatment Options for Pediatric Fractures
Treatment for pediatric fractures depends on the type and location of the break. Most child bone injuries heal well with proper care. Here are common treatment options:
Most children recover fully with the right care. However, always follow your doctor’s advice for the best results.
Prevention and Home Care Tips
While not all fractures can be prevented, you can lower the risk. Here are some tips to keep your child safe:
If your child has a fracture, home care is important. Keep the cast or splint dry and clean. Watch for swelling, pain, or changes in skin color. If you notice any problems, contact your doctor right away.
When to See a Doctor
Some signs mean you should seek medical help right away. Do not wait if your child has:
Quick treatment can prevent serious problems. Always trust your instincts if you think something is wrong.
Frequently Asked Questions
How long does it take for a child’s fracture to heal?
Most pediatric fractures heal in 3 to 8 weeks. However, healing time depends on the child’s age and the type of fracture.
Can a child return to sports after a fracture?
Yes, but only after the bone has healed. The doctor will let you know when it is safe to return to sports or play.
Are children’s bones more likely to break than adults’ bones?
Children’s bones are softer and more flexible. This means they can bend or break more easily, but they also heal faster.
What should I do if my child has a cast?
Keep the cast dry and clean. Check for swelling, pain, or changes in skin color. Contact your doctor if you notice any problems.
Do all fractures need surgery?
No, most pediatric fractures heal with casting or splinting. Surgery is only needed for severe or complicated breaks.
For more information, you can visit trusted sources like the CDC or WHO.
Consult a pediatric specialist for personalized guidance on pediatric fractures.